What is melamine
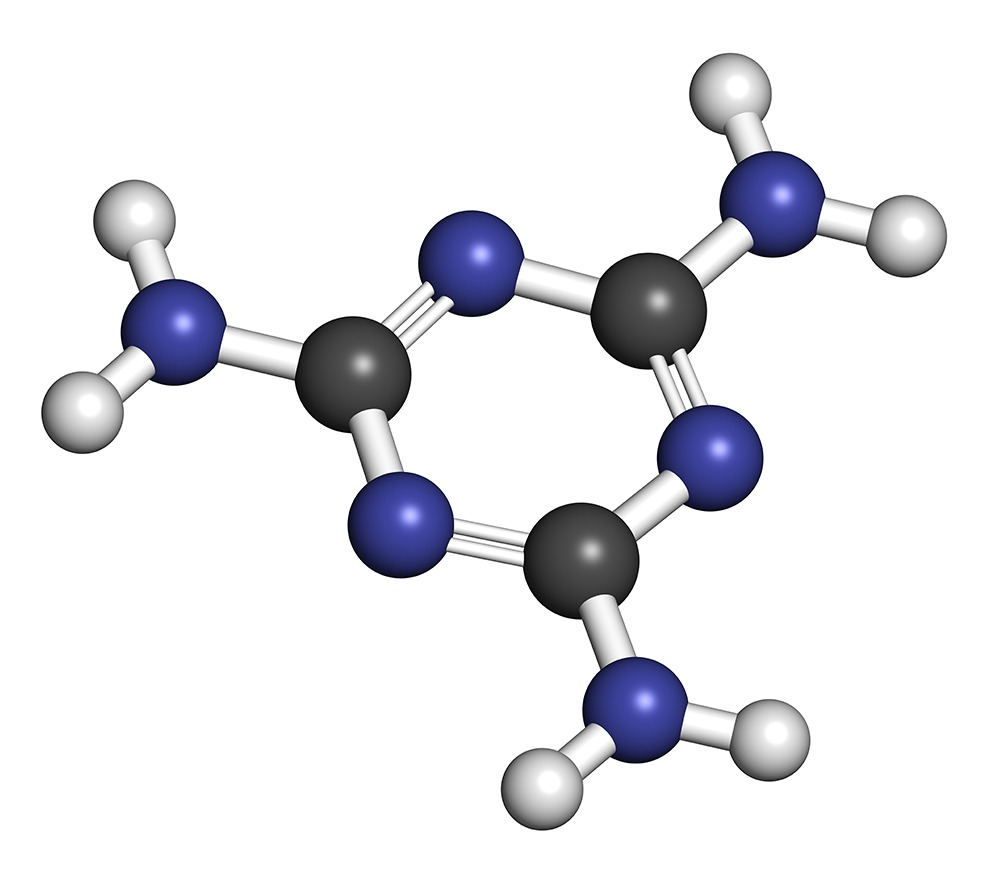
Melamine (CAS number 108-78-1) is an organic based substance. It is the most valuable and sophisticated product in the nitrogen chain. With 66% nitrogen content, Melamine has inherent flame retardant properties.
Being almost exclusively used as intermediate for thermosetting resins, melamine is an important raw material for the wood-based panel industry, delivering scratch-resistance for coatings and adding essential properties for moulding compounds. For more than 50 years, melamine in resins has been safely used in a variety of final end-user articles.
Historical background
Melamine was first synthesised by the German scientist Justus von Liebig in the 1830’s. Commercial interest and synthesis of the compound started in 1937 when melamine was first produced with urea as feedstock.
Today most melamine is still used as an intermediate in the decorative surfaces of wood-based panels and as a component of the glue that binds the wood chips or fibres together.
Applications
Melamine can be found in many things of our daily life. Some applications might be more familiar than others, but they all have in common that its unique properties help to make our life easier, more comfortable and safer.
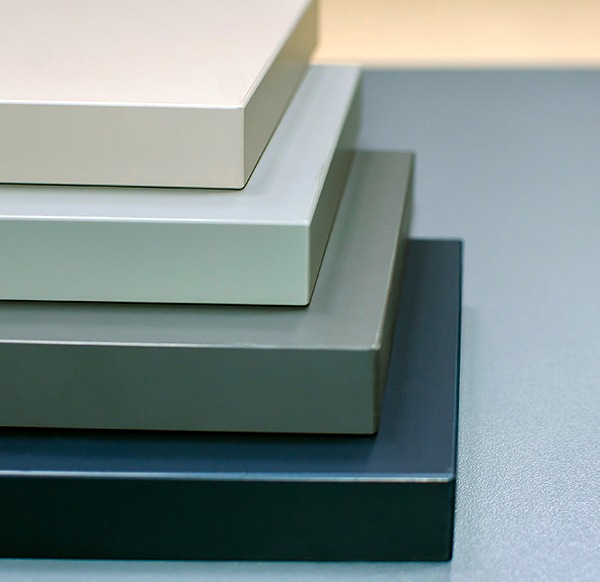
Melamine in Laminates
Melamine in wood adhesives
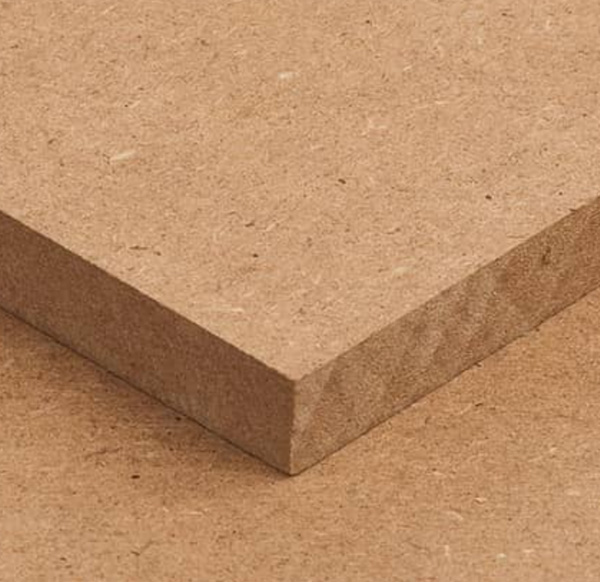
The wooden substrates mentioned above also contain melamine – plywood, particle boards (PB), medium density fibreboards (MDF) as well as high density fibreboards (HDF), oriented strand boards (OSB) or laminated veneer lumber (LVL) are bonded with melamine containing urea-formaldehyde (UF) adhesives. Also here melamine adds its unique properties to the product; it reduces the release of free formaldehyde, improves the water resistance of the boards.

Melamine in surface coatings
Specially formulated melamine resin systems are used to produce highly durable coatings. This includes clear finishes for paper, fabrics, wood and metals. By pigmenting the resin systems opaque enamel finishes can be obtained. You find them on refrigerators, washing machines, hospital equipment and kitchen utensils where they show their strengths: chemical and water resistance and mechanical properties like scratch resistance. One popular application is within the automotive industry. MF resins in coatings help to reduce solvent emissions and thus have a positive impact on the environment.
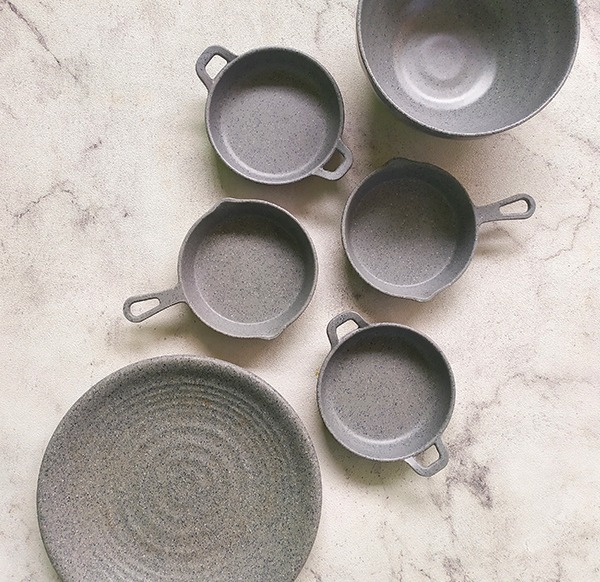
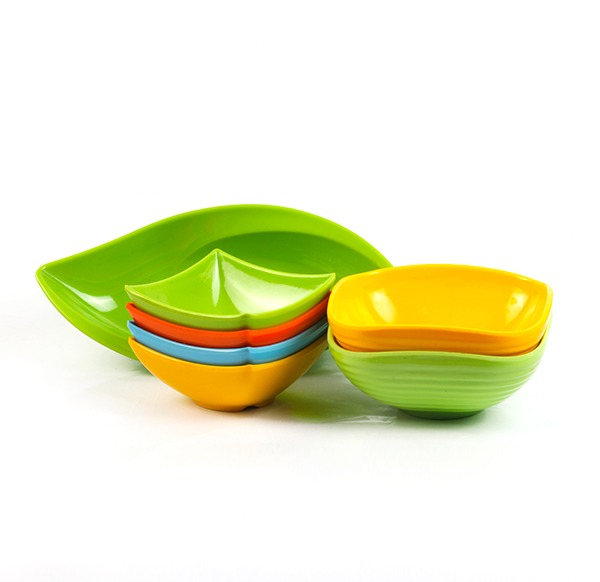
Melamine in Moulding Compounds
Melamine resins are strongly thermosetting and can be moulded into a variety of products for our daily life. The moulds are heat-resistant, odour- and tasteless as well as non-conductive. By adding pigments to the resin, various color and combinations thereof are possible. Final moulding products include house hold appliances, table- and dinnerware, utensil handles, electric sockets and much more.
Melamine in Textiles and Paper
Applied to textiles, MF resins improve wrinkle resistance and add flame-retardant properties. Paper treated with melamine is more resistant to wrinkle and impregnated against moisture. Best example are banknotes – despite years of intensive use, they do not wrinkle much and also survive the washing machine.
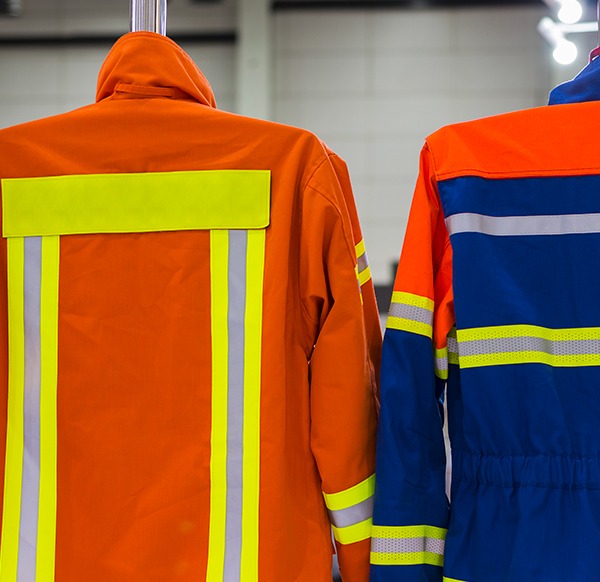
Flame retardants
Naturally melamine has a very high nitrogen content. This leads to sublimation or decomposition of the molecule when heated above a determined value. The sublimation or decomposition of melamine is absorbing considerable heat energy and thus serves as a heat sink in fire situations. Thus, melamine is an excellent alternative towards halogen-based flame retardants (FR). It is mainly used in specialized paints, textile products like firefighting apparel, and in flexible urethane foam that is used in the furniture and bedding industry as well as in electronics products.


Concrete plasticisers
Melamine also enters the fabrication of melamine poly-sulfonate used as a superplasticizer for making high-resistance concrete. Sulfonated melamine formaldehyde (SMF) is a polymer used as a cement admixture to reduce the water content in concrete while increasing the fluidity and the workability of the mix during its handling and pouring. It results in concrete with a lower porosity and a higher mechanical strength, exhibiting an improved resistance to aggressive environments and a longer lifetime.
Made in Europe
In Europe, melamine is manufactured according to high environmental, social and technical standards, guaranteeing a consistent, high quality. European producers strongly focus on safety in every aspect of their operations.
Buying European products is buying European standards
The EU aims to ensure everyone in Europe has access to better quality goods and services at lower prices, whilst at the same time safeguarding the environment. In terms of numbers, 27% of the global (~ 1,5 Mton per year) melamine consumption occurs in Europe.
Buying European products has many benefits, ranging from job creation to stimulating growth, minimising the ecological footprint and protecting consumers.